THE XERCES SOCIETY FOR INVERTEBRATE CONSERVATION Aquatic Invertebrates in Pacific Northwest Freshwater Wetlands |
| Identify taxa |
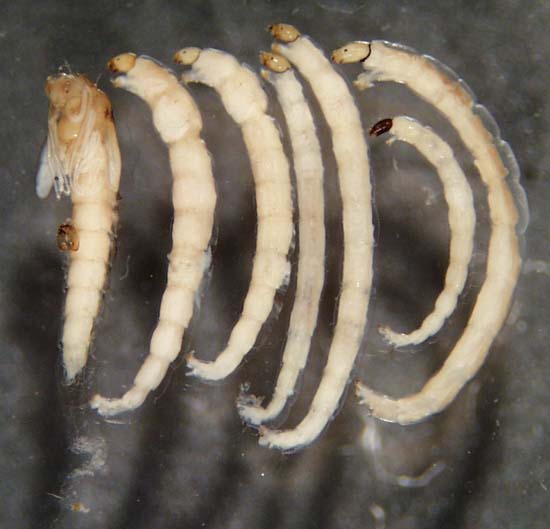
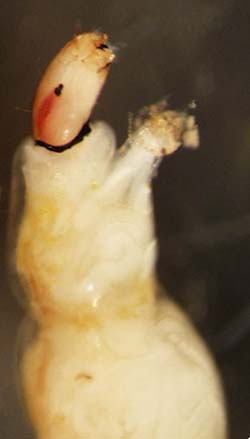
Ceratopogonidae |
     |
||
|
|||
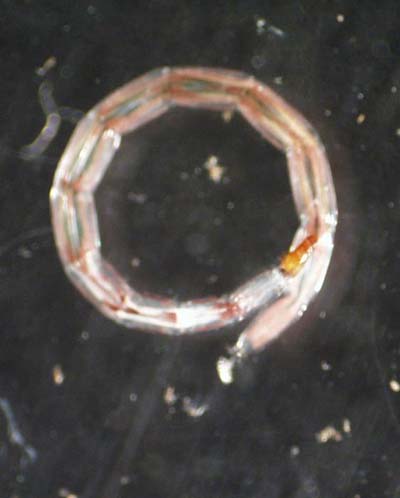
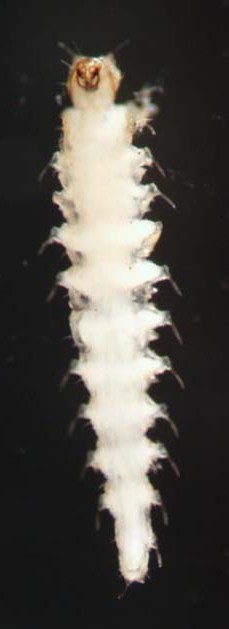
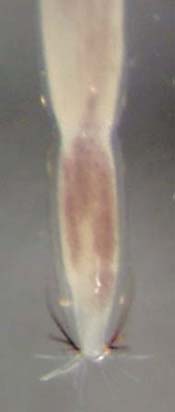
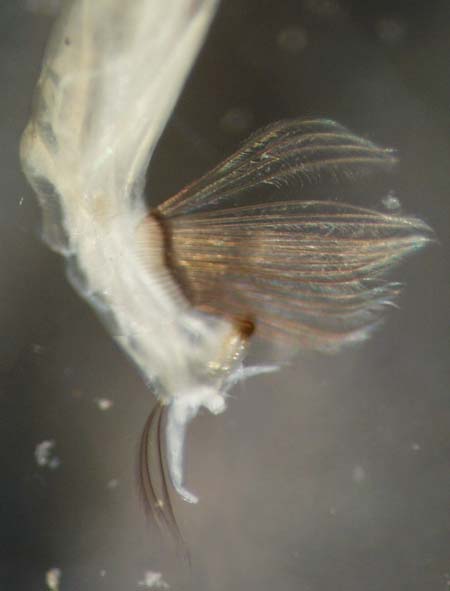
Chaoboridae |
   |
||
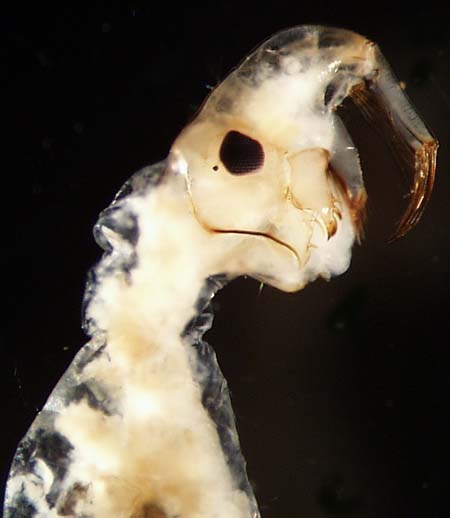
Chironomidae |
|||
|
|||
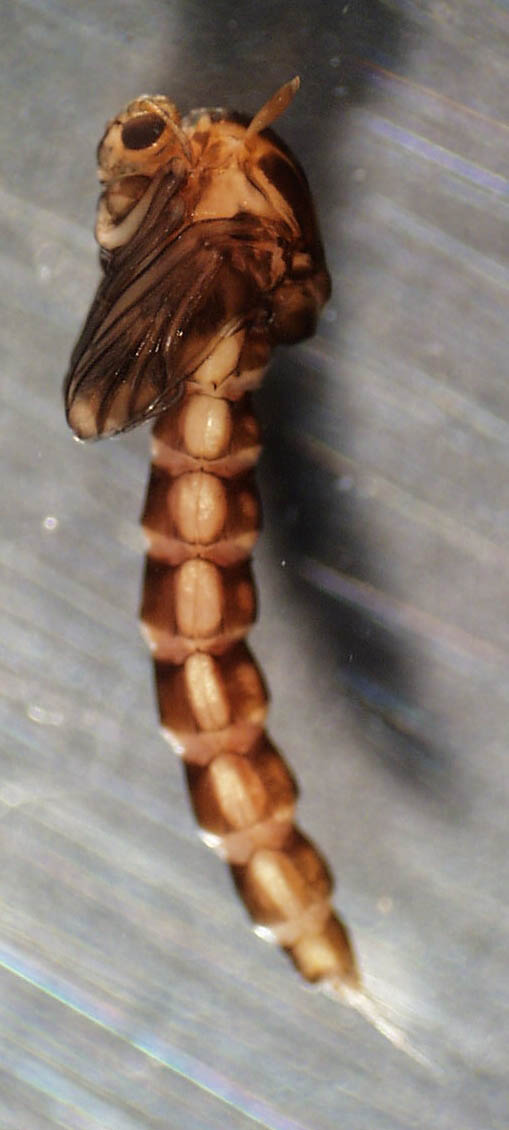
Culicidae |
  |
||
|
|||
Psychodidae |
     |
||
|
|||
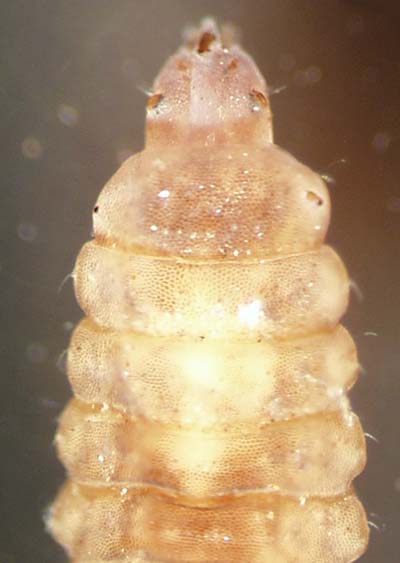
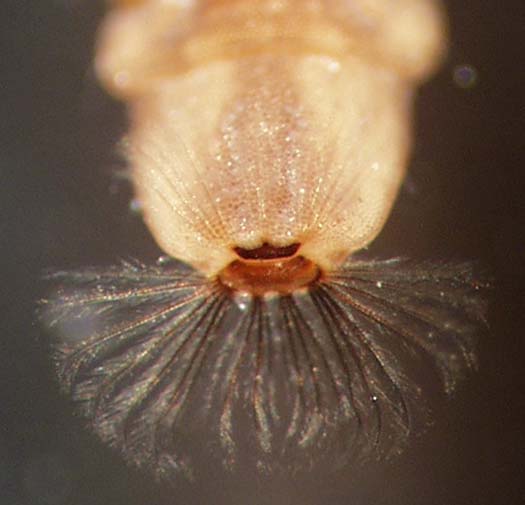
| Stratiomyidae (soldier flies) Well-developed head capsule; prominent spiracles. Head region distinct even if not sclerotized; thorax is wider than head; prolegs absent; body tough and leathery, segments not subdivided. |
    |
||
© 2007 Xerces Society
Contact info@xerces.org