THE XERCES SOCIETY FOR INVERTEBRATE CONSERVATION Aquatic Invertebrates in Pacific Northwest Freshwater Wetlands |
| Identify taxa |
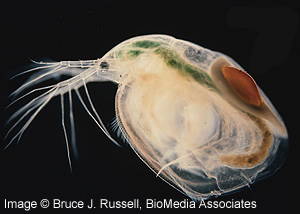
Water fleas primarily live in still waters, and are dominant in the plankton found in freshwater habitats. Cladocerans are small and generally have a distinct head and the carapace extends over the thorax and abdomen. Cladocerans in the family Chydoridae have been collected in wetlands in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. While cladocerans are primarily benthic. Their antennae are well developed and used as the primary swimming structures. Most eat algae, bacteria, debris, and microorganisms. Four families of Cladocera predate on zooplankton. Filter-feeding cladocerans are among a few known animals that can clear pollution-caused algal blooms in lakes. Moreover, water fleas are a critical part of freshwater ecosystems; most freshwater fish species and many bird species depend on water fleas as a significant source of food. |
Size: small Identifying feature(s): flattened ventrally with legs inside an expanded carapace Habitat: lakes, slow moving streams, ponds, puddles, estuaries, oceans Tolerance to pollutants: tolerant |
 |
|
© 2007 Xerces Society
Contact info@xerces.org